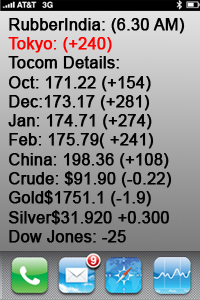
Introduction:
Tripura, a state in northeastern India, has emerged as a significant player in the rubber industry. The region’s favorable climatic conditions and extensive rubber plantations have positioned it as a key producer of natural rubber in the country. This essay aims to explore the dynamics of Tripura’s rubber prices, analyzing the factors that influence their fluctuations and their impact on the local economy. By delving into the various aspects of rubber cultivation, market forces, government policies, and global trends, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and opportunities that surround Tripura’s rubber industry.
Historical Background:
Rubber cultivation in Tripura has a rich history dating back to the early 20th century. The state’s abundant rainfall, moderate temperature, and suitable soil conditions provided a fertile ground for rubber plantations. In the 1950s, the government initiated programs to promote rubber cultivation, leading to increased production. Tripura’s rubber industry experienced significant growth during the 1980s and 1990s, fueled by the establishment of Rubber Board-managed plantations and the introduction of high-yielding hybrid varieties.
Factors Affecting Rubber Prices :
- Demand and Supply: The most crucial factor influencing rubber prices is the balance between demand and supply. Global demand for rubber, particularly from the automotive industry, has a substantial impact on Tripura’s rubber prices. Economic growth in emerging economies and fluctuations in crude oil prices also play a significant role in determining demand. Any disruptions in supply, such as adverse weather conditions or diseases affecting rubber trees, can have a substantial impact on prices.
- International Market Trends: Tripura’s rubber prices are closely linked to global market trends. The international prices of natural rubber, influenced by factors like geopolitical tensions, currency exchange rates, and trade policies, have a direct bearing on the local prices. Changes in prices of synthetic rubber, a substitute for natural rubber, can also impact demand and consequently affect Tripura’s rubber prices.
- Cost of Production: The cost of production is a critical determinant of rubber prices. Factors such as labor costs, fertilizers, pesticides, transportation, and energy expenses all contribute to the overall cost of rubber production. Any significant fluctuations in these costs can influence the pricing dynamics in Tripura’s rubber industry.
- Government Policies: Government policies and interventions play a significant role in shaping rubber prices. Subsidies, export-import regulations, taxation, and support for research and development initiatives can directly impact the profitability of rubber cultivation and subsequent pricing. Additionally, policies related to land acquisition, environmental regulations, and labor laws also influence the overall rubber production landscape.
Impact on the Local Economy:
The fluctuations in Tripura’s rubber prices have a significant impact on the state’s economy. Rubber cultivation provides livelihoods to a large number of farmers, particularly in rural areas. When rubber prices are high, farmers experience increased income, leading to improved living standards and economic growth at the local level. Conversely, during periods of low prices, farmers face financial challenges, impacting their well-being and overall economic stability.
The rubber industry also contributes to employment generation and the creation of ancillary businesses such as rubber processing units, transportation services, and rubber-based product manufacturing. Fluctuations in rubber prices can affect these sectors, leading to job losses or reduced economic activity.
Furthermore, the state’s revenue collection is also influenced by rubber prices. As the prices rise, the government receives increased tax revenues from rubber-related activities, which can be utilized for infrastructure development, education, healthcare, and other social welfare programs. Conversely, when prices decline, the government’s revenue stream is affected, leading to potential budgetary constraints.