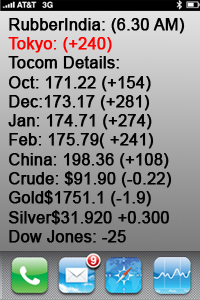
Current Market Overview:
Japanese rubber futures have experienced a slight decline, with the Osaka r May delivery falling by 0.59% to 368.8 yen per kg ($2.39) as of early trading today. This drop reflects ongoing concerns about global demand for rubber, particularly in light of disappointing economic data from China, the world’s largest consumer of the commodity.
Key Factors Influencing Prices:
Global Demand Concerns:
The May rubber on the SHFE also saw a decline, dropping 1.41% to 17,730 yuan ($2,429.47) per metric ton. This decline is attributed to weaker-than-expected consumption data from China, which raises doubts about future demand .
Economic Context:
Recent economic indicators from China have shown unexpected weakness, which could hinder economic growth. This situation is compounded by ongoing tariff threats and the slow impact of Beijing’s fiscal stimulus measures.
Oil Prices and Competition:
Falling oil prices, influenced by the U.S. Federal Reserve’s decision to slow interest rate cuts, add complexity to the rubber market. Natural rubber competes with synthetic rubber, which is derived from crude oil, making fluctuations in oil prices particularly impactful.
Currency Effects:
The Japanese yen has weakened, reaching a one-month low of 154.88 per dollar. This depreciation makes yen-denominated assets more attractive to foreign buyers, providing a cushion against the falling rubber prices driven by global demand concerns.
Market Sentiment:
The Nikkei index has also reacted negatively, falling 1.8% as investors anticipate the outcomes of the Bank of Japan’s upcoming policy meeting .
Conclusion:
The current landscape for Japanese rubber futures is characterized by a combination of declining prices due to global demand concerns and a weaker yen that may help mitigate some of the adverse effects. Investors should remain vigilant as economic conditions evolve, particularly in relation to China’s consumption patterns and global oil prices.
India:
The rubber price outlook for India remains uncertain as the market reacts to both local and international influences. While favorable weather conditions may improve yields, the overall production is likely to remain below previous levels. Stakeholders should be prepared for potential price volatility as global economic conditions evolve and local supply adjusts to changing demand dynamics.