July 30, 2025
Rubber India
Overview
Today, Japanese rubber futures have increased due to positive sentiments surrounding U.S.-China trade talks and a recovery in global automobile sales. However, high inventory levels are putting a cap on gains in the market.
Market Prices
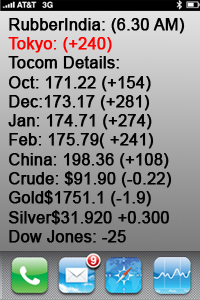
Osaka Exchange (OSE):
January delivery rubber contract rose by 0.6 yen (0.19%) to 322.5 yen ($2.18) per kg.
Shanghai Futures Exchange (SHFE):
September delivery rubber contract increased by 55 yuan (0.37%) to 15,030 yuan ($2,094.72) per metric ton.
September butadiene rubber contract remained unchanged at 11,855 yuan ($1,652.22) per metric ton.
Singapore Exchange (SICOM):
August delivery contract fell by 1% to 170.2 U.S. cents per kg.
Trade Talks and Tariff Updates
Recent discussions between U.S. and Chinese officials resulted in a mutual agreement to extend their 90-day tariff truce. This follows a similar agreement between the U.S. and the European Union, which has set tariffs at 15% on most goods—half of what was initially threatened.
Automobile Sales
Global automobile sales have shown a significant growth of 5% in the first half of 2025, marking the fifth consecutive month of growth in June. This uptick could positively influence rubber demand, as increased vehicle production typically requires more rubber for tires.
Inventory Levels
Despite the rise in automobile sales, high inventory levels are a concern. As of July 27, total inventory in the Qingdao area reached 640,400 tons, an increase of 6,000 tons (0.91%) from the previous period. This excess stock may pressure rubber prices in the near term.
Industry Insights
Factories in Thailand are currently hesitant to purchase more rubber due to adequate production stock and uncertainty surrounding upcoming U.S. tariffs, which are set to take effect on August 1.
Investors are closely monitoring U.S. Federal Reserve policy decisions and upcoming Chinese PMI data, which could impact market dynamics.
Company News
Nissan, a major Japanese automaker, announced plans to stop production at its Civac plant in Mexico by March 2026 as part of a global restructuring effort. This change will reduce Nissan’s global production capacity from 3.5 million vehicles to 2.5 million, decreasing the number of manufacturing sites from 17 to 10. This decision may further influence rubber demand as vehicle manufacturing adjusts.
Conclusion
In summary, while optimism surrounding trade talks and automobile sales is helping to boost rubber futures, the high levels of inventory are a significant factor keeping prices in check. Market participants should stay alert to economic indicators and industry developments that could affect rubber demand and pricing trends moving forward.