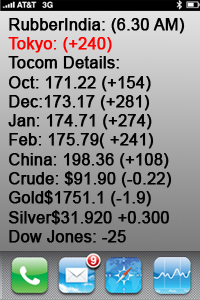
Market Overview
Natural rubber prices experienced a slight increase today, driven by concerns over potential supply disruptions in Thailand and rising oil prices. Despite these upward pressures, gains were limited due to a stronger yen and mixed market conditions.
Price Movements
Osaka June rubber rose by 0.4 yen (0.1%), reaching 384.2 yen ($2.47) per kg.
SHFEe March rubber increased by 170 yuan (0.99%), settling at 17,425 yuan ($2,376.80) per metric ton.
Butadiene Rubber: February contract surged by 485 yuan (3.41%), closing at 14,705 yuan ($2,005.78) per metric ton.
Supply Factors
The Thai meteorological agency reported that the northeast monsoon is expected to strengthen, bringing thunder showers and isolated heavy rains. This weather pattern poses a risk to rubber production in Thailand, the world’s top supplier, potentially affecting overall supply levels.
Oil Prices Influence
Oil prices rose over 2% on Wednesday, spurred by a significant draw in U.S. crude stockpiles and concerns over supply disruptions from new U.S. sanctions on Russia. Since natural rubber competes with synthetic rubber (derived from crude oil), fluctuations in oil prices often impact natural rubber pricing.
Currency Impact
The Japanese yen strengthened against the U.S. dollar, which decreased by 0.93% to 156.49 yen, following comments from the Bank of Japan’s governor regarding potential interest rate hikes. A stronger yen makes yen-denominated rubber assets less affordable for overseas buyers, which may temper price increases.
Market Sentiment
Despite the positive movement in rubber prices, stocks in China, a major consumer, closed lower as investors await further government stimulus measures. This cautious market sentiment may influence future demand for natural rubber.
Conclusion
Today’s price movements in the natural rubber market reflect ongoing supply concerns and rising oil prices, tempered by currency fluctuations and mixed market signals from China. The outlook remains vigilant as traders monitor developments in both supply conditions and global economic factors.